Sustainable Manufacturing: Building a Greener Future for Industry
Transforming production for environmental, economic, and social prosperity
Why It Matters: In an era where environmental consciousness is no longer optional, sustainable manufacturing has emerged as a critical imperative for businesses worldwide. As industries grapple with climate change, resource scarcity, and increasing regulatory pressures, the shift toward sustainable production practices represents not just an ethical choice, but a strategic necessity for long-term viability.
Understanding Sustainable Manufacturing
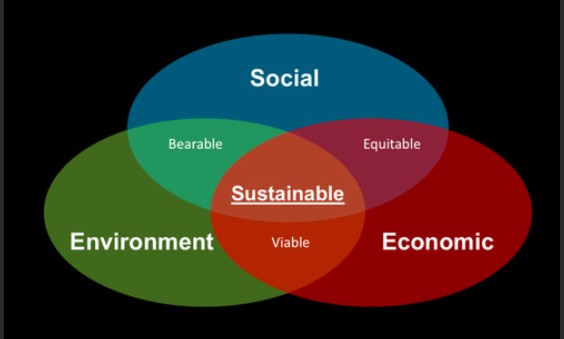
Sustainable manufacturing is a holistic approach to production that minimizes negative environmental impacts while conserving energy and natural resources. It's about creating products through economically sound processes that reduce pollution, enhance worker safety, and promote community wellbeing. At its core, sustainable manufacturing balances three crucial pillars: environmental responsibility, economic viability, and social equity.
The Three Pillars of Sustainable Production
Lean Manufacturing: Efficiency at Its Best
Lean manufacturing serves as a cornerstone of sustainable production by eliminating waste in all its forms. This methodology focuses on streamlining operations, reducing unnecessary steps, and optimizing resource utilization. By cutting out waste in time, materials, and energy, lean principles naturally align with sustainability goals while simultaneously improving profitability.
Green Manufacturing: Environmental Stewardship
Green manufacturing takes environmental protection to the forefront. This approach emphasizes the reduction of pollution, emissions, and waste throughout the production cycle. Companies adopting green manufacturing practices invest in cleaner technologies, renewable energy sources, and processes that minimize their ecological footprint. The result is a production system that works in harmony with nature rather than against it.
Sustainable Manufacturing: The Complete Integration
True sustainable manufacturing synthesizes lean and green approaches while incorporating broader considerations of social responsibility and long-term economic sustainability. It's not just about being efficient or environmentally friendly—it's about creating a comprehensive system that endures and benefits all stakeholders.
Key Components of Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
Implementing sustainable manufacturing requires attention to six critical areas that work together in an interconnected system:
Environmental Impact: Reducing carbon emissions, minimizing ecological disruption, and protecting natural resources form the foundation of sustainable operations. This involves conducting thorough environmental assessments and continuously working to lessen negative impacts.
Manufacturing Cost: Sustainability doesn't mean sacrificing profitability. By optimizing processes and reducing waste, companies often discover that sustainable practices lead to significant cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced material consumption.
Energy Consumption: Energy efficiency stands as one of the most impactful areas for sustainability improvement. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, upgrading to energy-efficient equipment, and optimizing production schedules can dramatically reduce both costs and environmental impact.
Waste Management: Effective waste management involves not just disposal but prevention. This includes implementing recycling programs, finding creative uses for byproducts, and designing processes that generate minimal waste from the outset.
Operational Safety: A truly sustainable operation prioritizes worker safety and wellbeing. Safe working conditions reduce accidents, improve morale, and contribute to long-term business stability.
Personnel Health: Beyond immediate safety concerns, sustainable manufacturing considers the long-term health impacts on workers, including exposure to chemicals, ergonomic factors, and overall workplace wellness.
Core Strategies for Achieving Sustainability
Several key strategies drive sustainable manufacturing success:
Optimization of Production Processes: Continuously analyzing and refining production techniques to eliminate inefficiencies and reduce resource consumption is fundamental to sustainable manufacturing.
Increased Energy Efficiency: Implementing smart energy management systems, upgrading equipment, and utilizing renewable energy sources can dramatically reduce both environmental impact and operational costs.
Producing Less Pollution, Emission, and Waste: Through cleaner production technologies and circular economy principles, manufacturers can significantly reduce their environmental footprint.
Industrial Symbiosis: This innovative approach involves creating networks where waste or byproducts from one company become valuable inputs for another, effectively closing resource loops and minimizing overall waste.
Design for Remanufacturing: Products designed with their end-of-life in mind can be more easily disassembled, refurbished, and remanufactured, extending product lifecycles and reducing resource consumption.
The Circular Economy Approach
Central to sustainable manufacturing is the concept of the circular economy, which challenges the traditional linear "take-make-dispose" model. This framework emphasizes:
Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste generation at every stage of production through careful planning and efficient processes.
Recycling: Establishing robust systems to reclaim and reprocess materials, keeping valuable resources in use.
Re-use: Designing products and packaging for multiple use cycles, extending their functional life.
Reduce: Cutting down on material and energy inputs through innovative design and process optimization.
Recover: Capturing energy and materials from waste streams that would otherwise be lost.
Re-design: Reimagining products to be more sustainable from conception, considering their entire lifecycle.
Re-manufacture: Building systems to restore used products to like-new condition, offering them new life and value.
Building a Sustainable Manufacturing Culture
Achieving true sustainability requires more than just technological changes—it demands a comprehensive cultural shift that encompasses the entire organization and its ecosystem:
Sustainability Indicators, Policies, and Procedures: Establishing clear metrics, formal policies, and standardized procedures ensures that sustainability goals are measurable, consistent, and integrated into daily operations.
Company Procedures, Culture, and Conditions: Creating an organizational culture that values sustainability requires leadership commitment, employee engagement, and embedding environmental responsibility into the company's DNA.
Sustainable Design: Incorporating sustainability principles from the initial design phase ensures that products are inherently more environmentally friendly throughout their lifecycle.
Supplier Attitudes and Support: A sustainable supply chain is essential. This means working with suppliers who share sustainability values and actively support environmental initiatives.
Customer Attitudes and Support: Educating customers about sustainable products and practices creates market demand for responsible manufacturing and builds brand loyalty.
Environmental Controls, Monitoring, and Remediation: Implementing robust environmental management systems ensures compliance, tracks progress, and addresses issues proactively.
Community Engagement: Sustainable manufacturers recognize their role as corporate citizens, engaging with local communities and contributing to broader sustainability efforts.
The Business Case for Sustainable Manufacturing
While the environmental and social benefits of sustainable manufacturing are clear, the business advantages are equally compelling. Companies that embrace sustainability often experience reduced operating costs through improved efficiency and waste reduction, enhanced brand reputation attracting environmentally conscious consumers, improved regulatory compliance reducing legal risks and penalties, increased innovation as sustainability challenges drive creative solutions, better employee retention and recruitment as workers increasingly seek purpose-driven employers, and long-term resilience by reducing dependence on scarce resources and volatile energy markets.
Looking Forward
Sustainable manufacturing is not a destination but a journey of continuous improvement. As technology advances and our understanding of environmental impacts deepens, manufacturers must remain adaptable and committed to evolving their practices. The integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, Internet of Things sensors, and advanced materials science promises to unlock new opportunities for sustainability.
The transition to sustainable manufacturing represents one of the most significant industrial transformations of our time. Companies that embrace this change position themselves not just as environmentally responsible actors, but as forward-thinking leaders prepared for the challenges and opportunities of the future. In a world increasingly defined by resource constraints and climate imperatives, sustainable manufacturing isn't just good ethics—it's good business.
The question is no longer whether to adopt sustainable manufacturing practices, but how quickly and effectively organizations can transform their operations to meet the demands of a changing world. The future of manufacturing is sustainable, and that future is now.

Leave a Comment